Mechanical Pumps
Mechanical Pumps
"A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action. "
Or
"The hydraulic machines which convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy are called pumps."
Types of Pumps-
The pumps are generally two types-
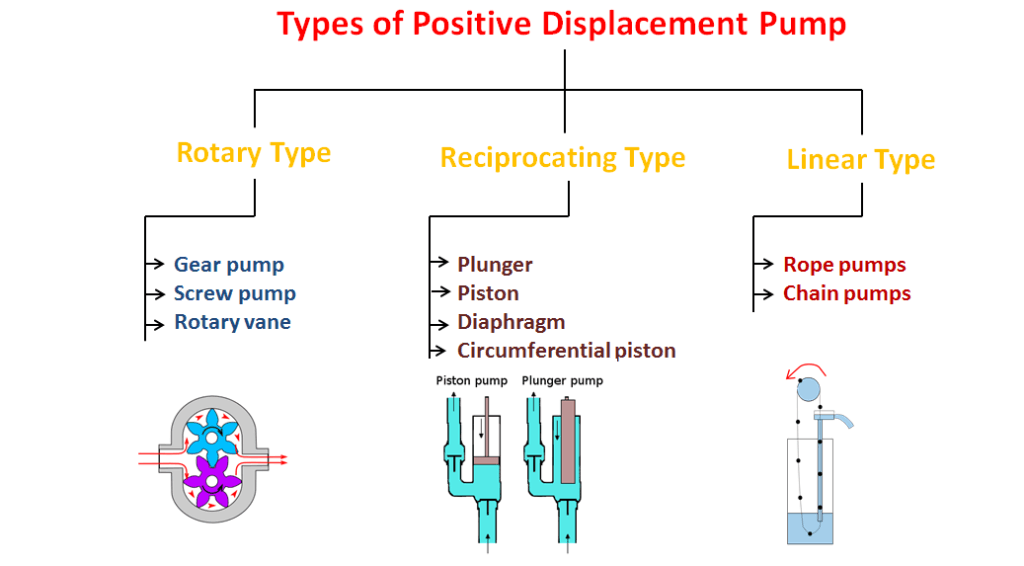
1. Positive Displacement Pumps
(a) Rotary types Pumps
(b) Reciprocating Types Pumps
(c) Linear types Pumps
2. Dynamic Pumps
(a) Centrifugal Pumps-
(i)Axial Flow
(ii) Mixed Flow
(iii) Peripheral Centrifugal Pumps
(b) Special Effect Pumps
(i) Jet Pumps
(ii) Electromagnetic Pumps
Other Classification of pumps-
1. On the basis of method of displacement of fluid
1. Positive displacement pumps
(a) Rotary Types Pumps-
(i) Internal Gear Pumps
(ii) Screw Pumps
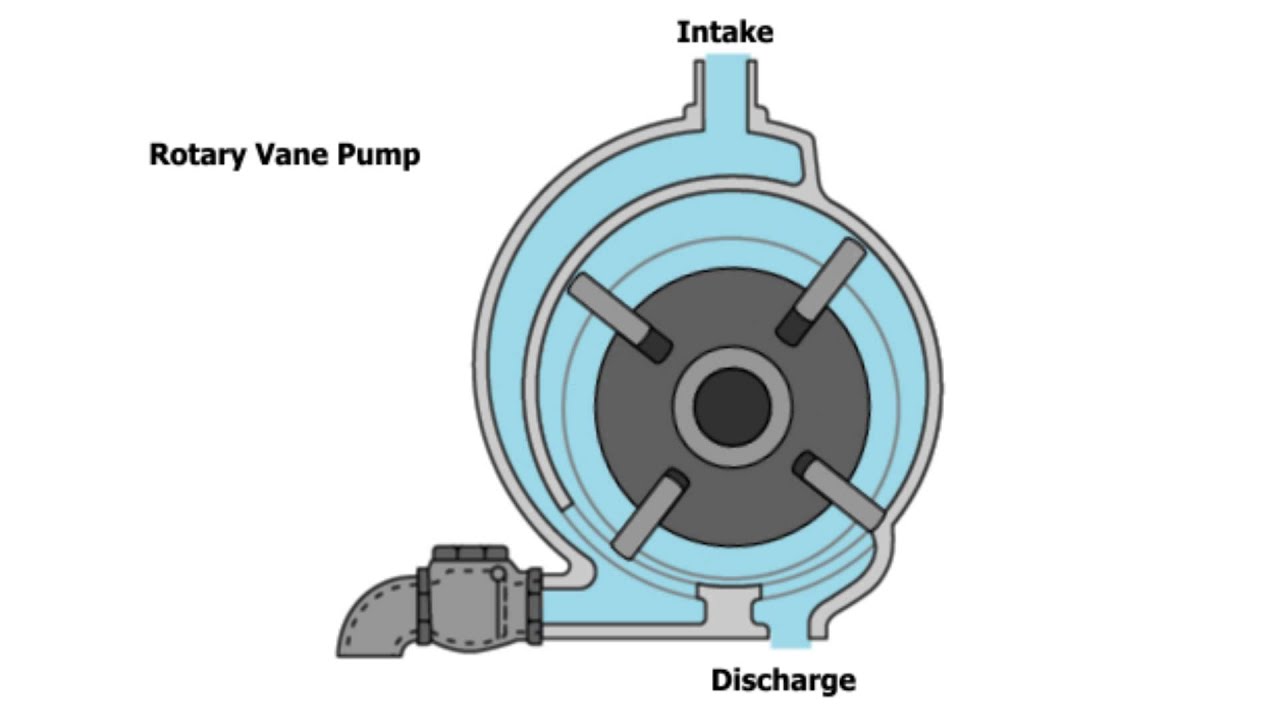
(iii) Rotary Vane Pumps
(iv) Flexible Vane or Sliding Vane Pumps
(v) Shuttle Block Pumps
(vi) Helical Twist Root Pumps
(vii) Liquid Ring Pumps
(viii) Flexible Impeller Pumps
(b) Reciprocatory Types Pumps-
(i) Plunger Pumps
(ii) Piston Pumps
(iii) Diaphragm Pumps
(iv) Circumferential Piston Pumps
According to the water being in contact with one side or both sides of piston
(i) Single Acting Pumps
(ii) Double Acting Pumps
According to Number of cylinder provided
(i) Single Cylinder Pumps
(ii) Double Cylinder Pumps
(iii) Triple Cylinder Pumps
(c) Linear Types Pumps-
(i) Rope Pumps
(ii) Chain Pumps
2. Impulse pumps3. Velocity pumps
4. Gravity pumps
5. Valveless pumps
2. On basis of number of impellers-
(a) Single Stage Pumps
(b) Double Stage Pumps
(c) Multi Stage Pumps
3. On the Basis of types of Flow
(a) Axial Flow Pumps
(b) Radial Flow Pumps
(c) Mixed Flow Pumps
1. On the basis of method of displacement of fluid:-
1. Positive Displacement Pumps-
A positive displacement pump makes a fluid move by trapping a fixed amount and forcing (displacing) that trapped volume into the discharge pipe.
Or
Positive displacement pump (PDP) is a type of pump in which a moving fluid is captured in a cavity and then discharges that fixed amount of fluid. The displacement of fluid takes place by some parts like plunger, piston, diaphragm etc. some of these pumps have expanding cavity at the suction side and a decreasing cavity at the discharge side. The liquid is sucked at the inlet side when the cavity expands and discharges it when the cavity decreases.
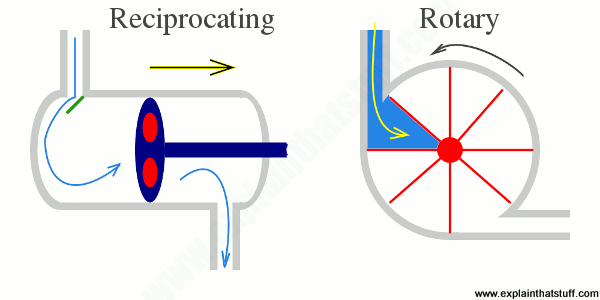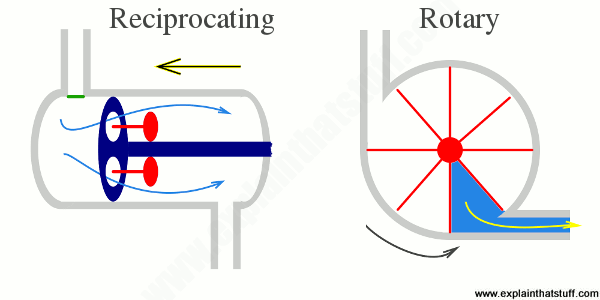
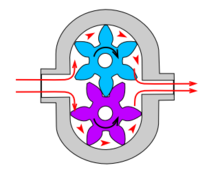
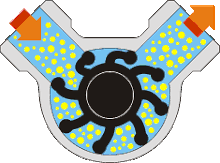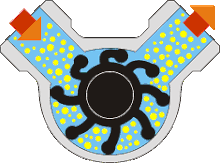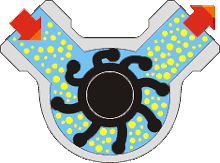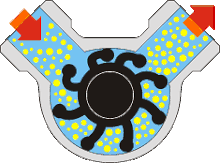
(a) Rotary Types Pumps- In this pump the fluid is moved by the use of a rotary part. It is the rotation which displaces the fluid from reservoir to the discharge pipe.
(i) Internal Gear Pumps- In this pump, the fluid is moved in between two rotating gears. The liquid is pushed between these two gears as it rotates.
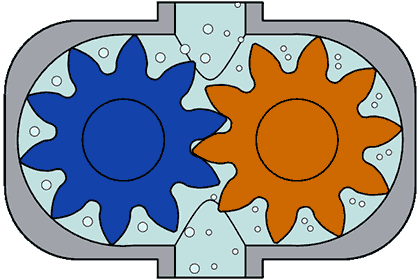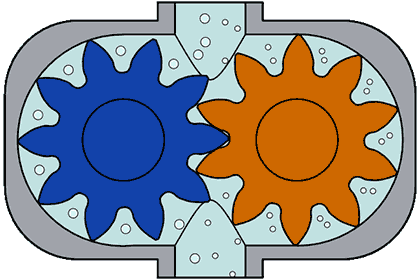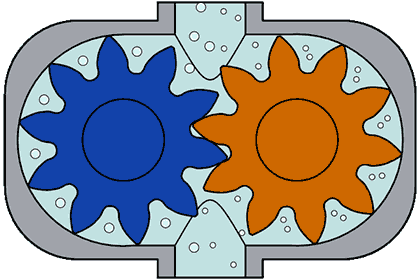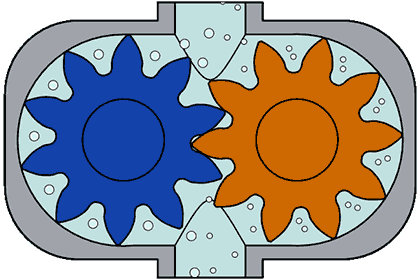
(ii) Screw Pumps- These pumps consist of two screw type rotor turning against each other. When the two screw rotates it sucks the water from the inlet and pump it to the outlet.

(iii) Rotary Vane Pumps- It is similar to scroll compressors. It consist of cylindrical rotor having vanes on it which is encased in a similar (i.e. cylindrical type) shaped housing. When it rotates the vanes on the rotor traps the fluid in between the rotor and casing and discharges it through outlet.
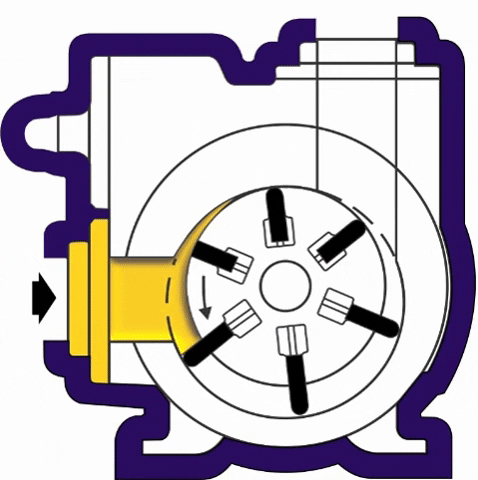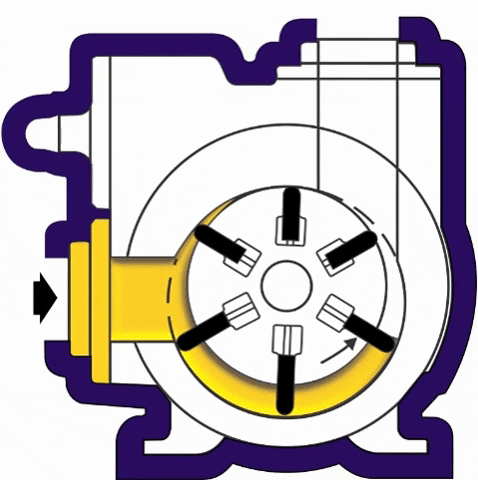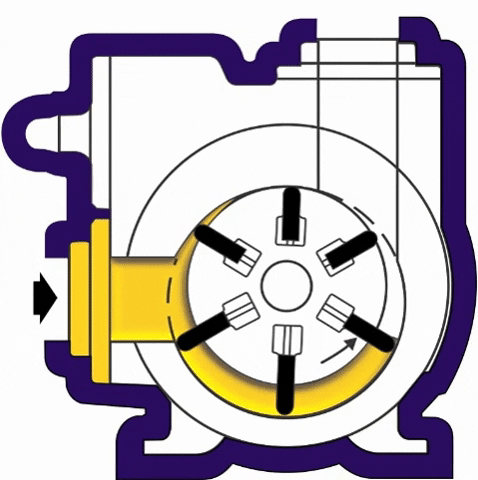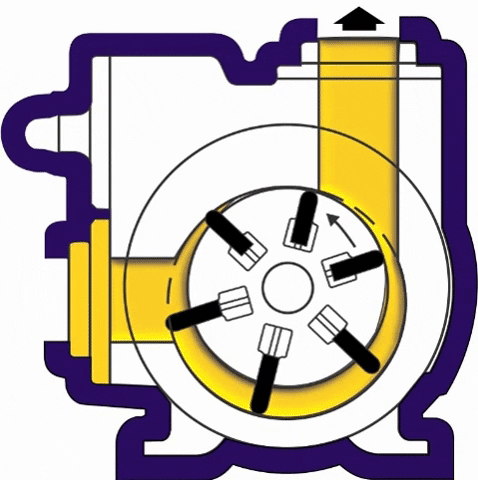
(iv) Flexible Vane or Sliding Vane Pumps- Sliding Vane Pumps have a number of vanes that are free to slide into or out of slots in the pump rotor, creating pumping chambers. Sliding Vane Pumps have strong suction and dry run capabilities, and provide superior energy saving advantages in process applications.

(v) Shuttle Block Pumps- The Shuttle Block Pump works on a unique pumping principle - a combination of Rotary and Reciprocating action.There are only three pumping elements - Rotor, Piston and Shuttle. Rotor is keyed to a single shaft and runs concentric in pump casing.

(vi) Helical Twist Root Pumps- In his types of pump there are two opposite types of impeller pump casing at an angle.
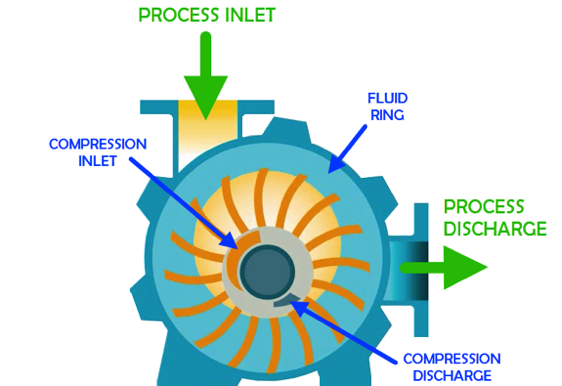
(vii) Liquid Ring Pumps- The function of a liquid-ring pump is similar to a rotary vane pump, with the difference being that the vanes are an integral part of the rotor and churn a rotating ring of liquid to form the compression-chamber seal. They are an inherently low-friction design, with the rotor being the only moving part. Sliding friction is limited to the shaft seals. Liquid-ring pumps are typically powered by an induction motor.
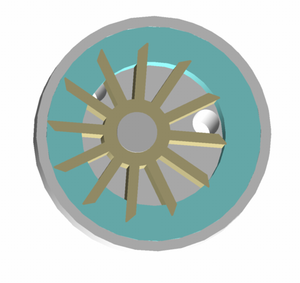

(viii) Flexible Impeller Pumps- A flexible impeller pump is a positive-displacement pump that, by deforming impeller vanes, draws the liquid into the pump housing and moves it to the discharge port with a constant flow rate. The flexibility of the vanes enables a tight seal to the internal housing, making the pump self-priming, while also permitting bi-directional operation. The output from these pumps tends to be smooth or gentle when compared to the operation of a reciprocating pump.
(b) Reciprocatory Types Pumps-
(i) Plunger Pumps- A plunger is used for pumping water.
(ii) Piston Pumps- It has piston for pumping fluid.

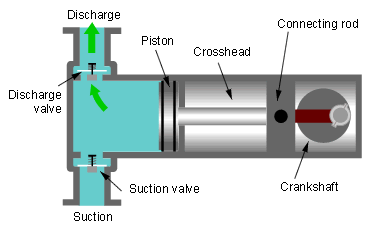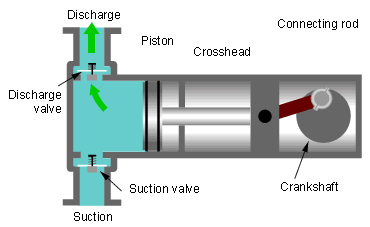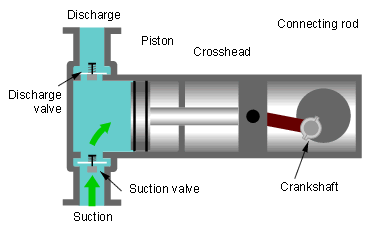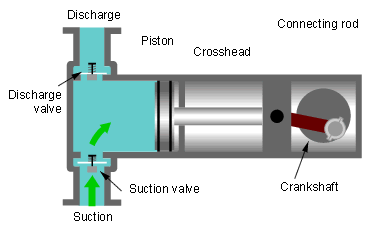
(iii) Diaphragm Pumps- It works same as plunger pump But it has diaphragm for suction and discharge of liquid. Diaphragm valves are used to pump hazardous and toxic fluids.


(iv) Radial Piston Pumps (Circumferential Piston Pumps) The hydraulic pump where pistons extend in a radial direction.

According to the water being in contact with one side or both sides of piston
(i) Single Acting Pumps- In this, suction takes place in one direction motion of the piston and discharge in other direction.

(ii) Double Acting Pumps- Suction and discharge takes place in both directions.
According to Number of cylinder provided
(i) Single Cylinder Pumps- When only single cylinder is used in reciprocating pump.
(ii) Double Cylinder Pumps- When two cylinder is used in reciprocating pump.
(iii) Triple Cylinder Pumps- When three cylinder is used in reciprocating pump.
(c) Linear Types Pumps-
(i) Rope Pumps- A rope pump is a kind of pump where a loose hanging rope is lowered into a well and drawn up through a long pipe with the bottom immersed in water.

(ii) Chain Pumps- The chain pump is type of a water pump in which several circular discs are positioned on an endless chain. One part of the chain dips into the water, and the chain runs through a tube, slightly bigger than the diameter of the discs. As the chain is drawn up the tube, water becomes trapped between the discs and is lifted to and discharged at the top.
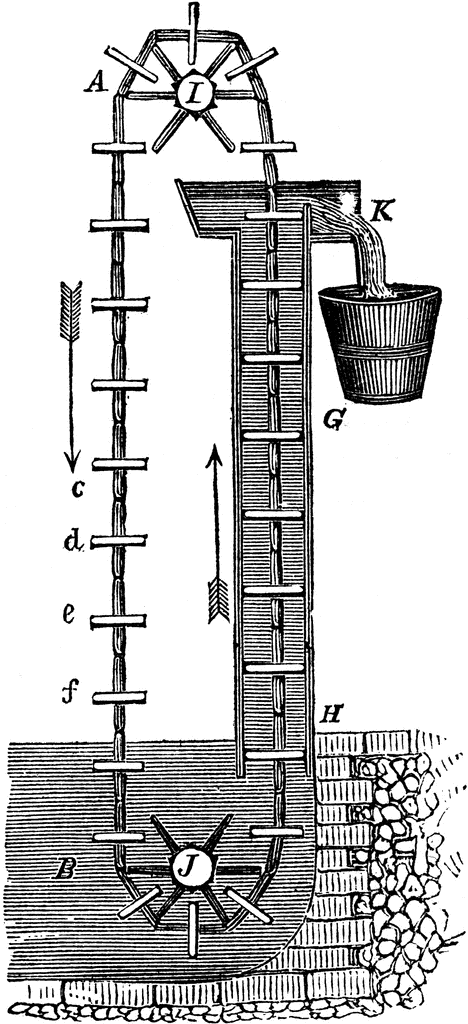
2. Impulse pumps- Impulse pump is operated by the pressure created by the gas (usually air ). In some of these pumps the gas is trapped in the liquid (mostly in water), is released and accumulated somewhere in the pump, this creates pressure that pushes part of liquid upwards. For example: hydraulic ram pumps, pulser pumps and airlift pumps.
- Hydraulic ram pumps – kinetic energy of a low-head water supply is stored temporarily in an air-bubble hydraulic accumulator, then used to drive water to a higher head.
- Pulser pumps – run with natural resources, by kinetic energy only.
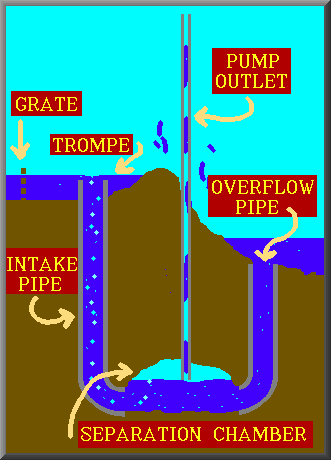
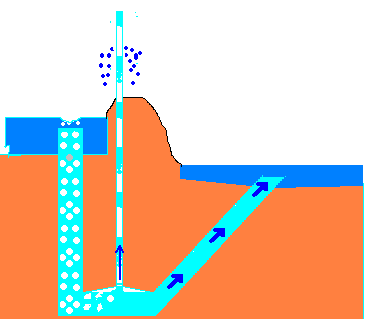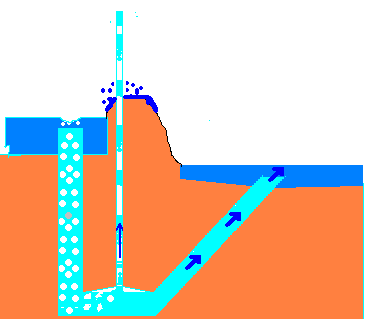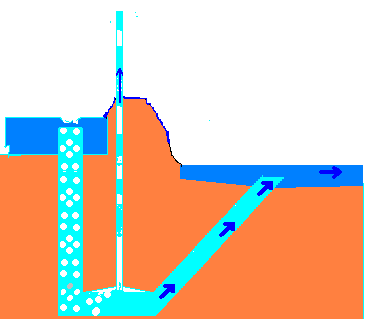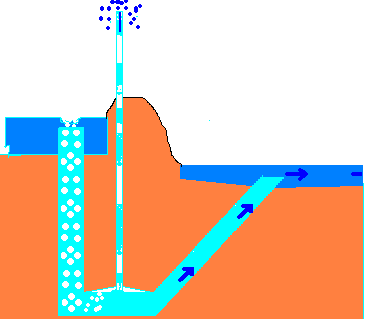
- Airlift pumps – run on air inserted into pipe, which pushes the water up when bubbles move upward.

3. Velocity pumps- In velocity pumps, the kinetic energy is added to the fluid by increasing the flow velocity. This gain in kinetic energy is converted into potential energy (pressure) by decreasing the velocity as the flow exits the pump into the discharge pipe. For example: rotordynamics pumps such as centrifugal pump.


4. Gravity pumps- The pump in which the flow of fluid takes place with the help of gravity is called gravity pumps. For example – syphon and heron’s fountain.

5. Valveless pumps- It is a pump in which the valves are not present and the flow of water takes place in the absence of valves. For example – impedance pump.


2. On basis of number of impellers:-
(a) Single Stage Pumps- A pump with one impeller rotating in its casing is called as single stage pump.

(b) Double Stage Pumps- A pump with two impellers rotating in its casing is called as double stage pump.

(c) Multi Stage Pumps- When a pump has more than two impellers in its casing than it is called as multi stage pump.
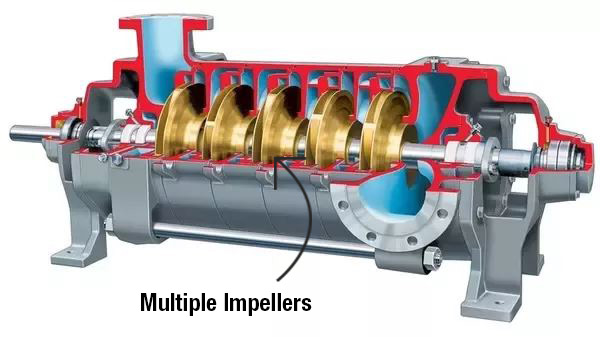
3. On the Basis of types of Flow:-
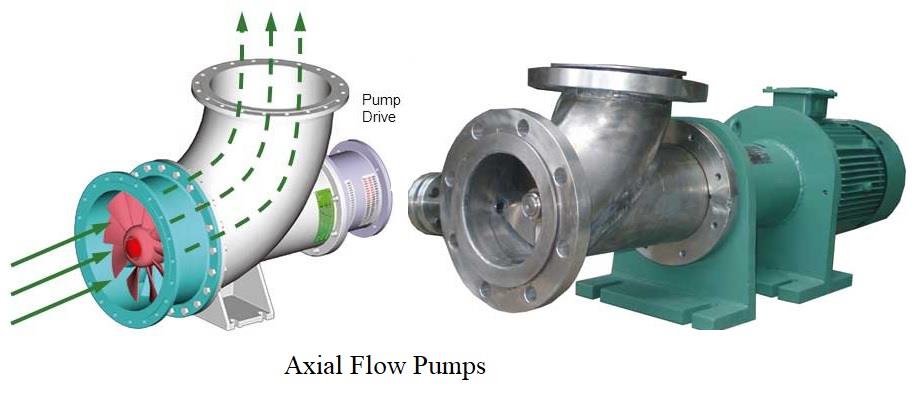
(a) Axial Flow Pumps- It is a pump in which the flow of water takes place axially (i.e. parallel to the axis of rotation).
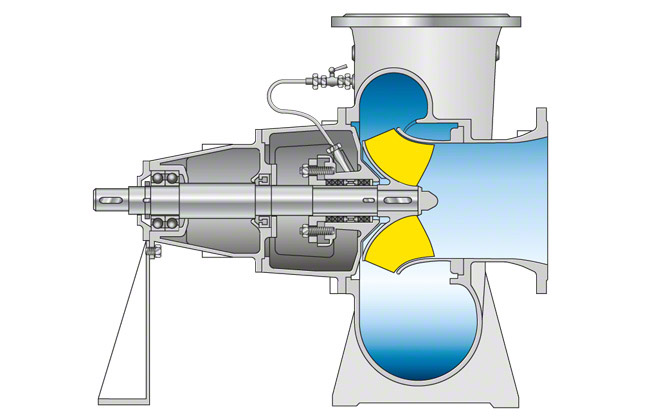
(b) Radial Flow Pumps- In these types of pumps the flow of fluid takes place in radial direction i.e. at right angles to the axis of rotation.
(c) Mixed Flow Pumps- In these pumps, the fluid enters axially and comes out radially or vice versa. It is a combination of axial and radial flow pumps.










Comments
Post a Comment