Total Quality Management
Total Quality Management
A core definition of total quality management (TQM) describes a management approach to long-term success through customer satisfaction. In a TQM effort, all members of an organization participate in improving processes, products, services, and the culture in which they work.
Or
A system of management based on the principle that every member of staff must be committed to maintaining high standards of work in every aspect of a company's operations.
The key principles of Total Quality Management
Commitment from the management:
- Plan (drive, direct)
- Do (deploy, support, and participate)
- Check (review)
- Act (recognize, communicate, revise)
Employee Empowerment
- Training
- Excellence team
- Measurement and recognition
- Suggestion scheme
Continuous Improvement
- Systematic measurement
- Excellence teams
- Cross-functional process management
- Attain, maintain, improve standards
Customer Focus
- Partnership with Suppliers
- Service relationship with internal customers
- Customer-driven standards
- Never compromise quality
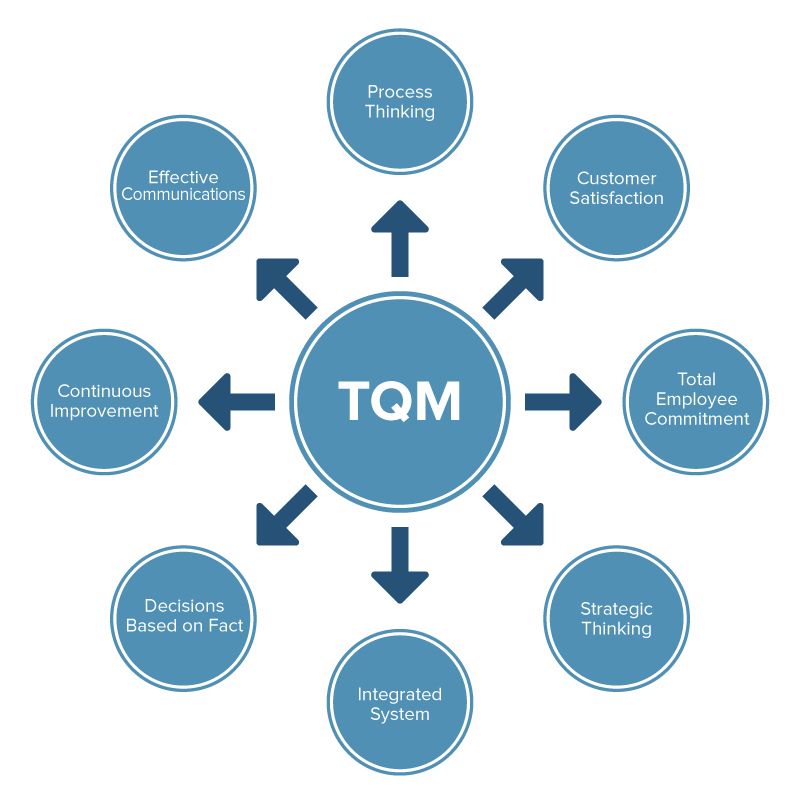
Benefits of Total Quality Management
The benefits arising from the implementation of a Total Quality Management in an organization are:
1. This will increase the awareness of quality culture within the organization.
2. A special emphasis on teamwork will be achieved.
3. TQM will lead to a commitment towards continuous improvement.
Essential requirements for successful implementation of TQM
1. Commitment: Quality improvement (in all aspect) must be everyone’s job in the organization. An apparent commitment from the top management, breaking down the barriers for continuous quality improvement and steps required to provide an environment for changing attitudes must be provided. Training and support for this should be extended.
2. Culture: There should be proper training to effect the changes in attitude and culture.
3. Continuous Improvement: Recognize improvement as a continuous process, and not merely a one-off program.
4. Customer Focus: Perfection in service with zero defectives and full satisfaction to end-user whether it’s internal or external.
5. Control: Ensure monitoring and control checks for any deviation from the intended course of implementation.
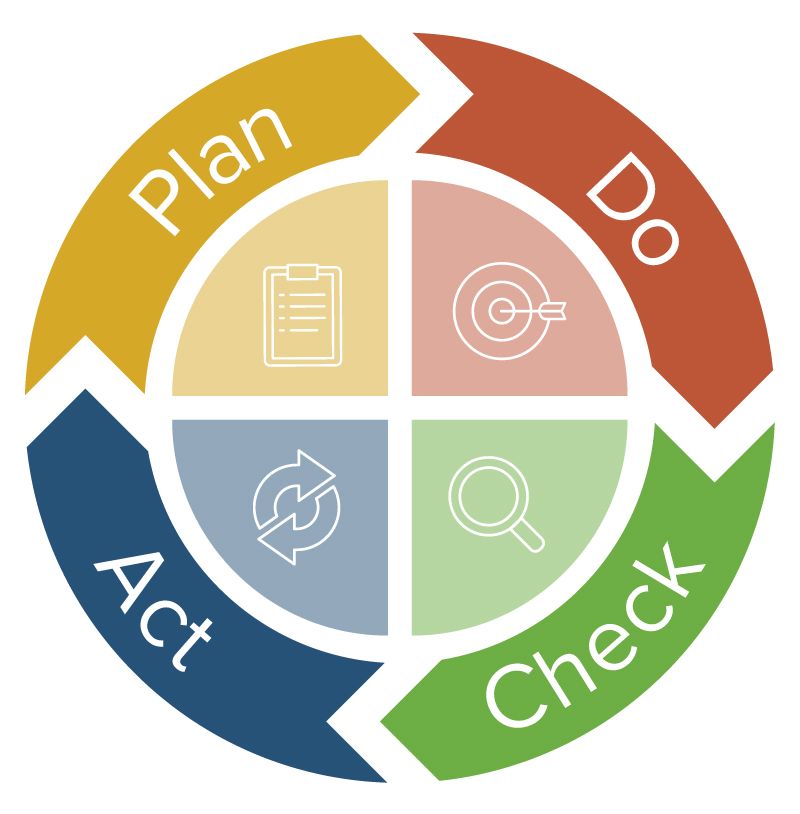
-Plan
-Do
-Check
-Act
This also referred to as the PDCA cycle.
1. Planning Phase: This phase is the most crucial phase of total quality management. Under this phase, employees have to come up with their respective queries and problems which need to be addressed. The employees apprise the management of different challenges which they are facing in their day to day operations and also analyze the root cause of the problem. They need to do the required research and collect significant data which would help them find solutions to all the problems.
2. Doing Phase: In this phase, a solution for the identified problems in the planning phase is developed by the employees. Strategies are devised and implemented to crack down the challenges faced by employees. The efficiency and effectiveness of solutions and strategies are also evaluated in this stage.
3. Checking Phase: Under this phase, a comparison analysis of before and after is done in order to assess the effectiveness of the processes and measure the results.
Acting Phase: This is the last phase of the cycle, in this phase employees document their results and prepare themselves to address other problems.
4. Act Phase: The acting phase is the presentation or the documentation of the results to let everybody know, ‘Hey, here’s how we were doing it. Here’s how it is now. This is the new way, and this is what this should address going forward."
Beliefs about Total Quality Management
Following are the universal Total Quality Management beliefs:
1. Satisfaction of the customer/owner is the measure of quality.
2. Everyone is an owner.
3. Continuous Quality improvement must be there.
4. Analysis of the processes is the key to quality improvement.
5. Constant TQM is not possible without consistent, active and enabling leadership by managers at all levels.
6. It is important to incessantly improve quality of the products and services which we are supposed to provide to our customers/owners.
Advantages of TQM
(i) Sharpens Competitive Edge of the Enterprise:
TQM helps an organisation to reduce costs through elimination of waste, rework etc. It increases profitability and competitiveness of the enterprise; and helps to sharpen the organisation’s competitive edge, in the globalized economy of today.
(ii) Excellent Customer Satisfaction:
By focusing on customer requirements, TQM makes for excellent customer satisfaction. This leads to more and more sales, and excellent relations with customers.
(iii) Improvement in Organisational Performance:
Through promoting quality culture in the organisation, TQM lead to improvements in managerial and operative personnel’s performance.
(iv) Good Public Image of the Enterprise:
TQM helps to build an image of the enterprise in the minds of people in society. This is due to stress on total quality system and customers’ requirements, under the philosophy of TQM.
(v) Better Personnel Relations:
TQM aims at promoting mutual trust and openness among employees, at all levels in the organisation. This leads to better personnel relations in the enterprise.
Limitations of TQM:
The philosophy of TQM suffers from the following major limitations:
(i) Waiting for a Long Time:
TQM requires significant change in organisation; consisting of:
1. Change in methods, processes etc. of organisation.
2. Change in attitude, behaviour etc. of people
Launching of TQM and acceptance of the philosophy of TQM requires a long waiting for the organisation. It is not possible to accept and implement TQM overnight.
(ii) Problem of Labour Management Relations:
Success of TQM depends on the relationships between labour and management; because participation of people at all levels is a pre-requisite for TQM programme implementation. In many organisations, here and abroad, labour-management relations are quite tense. As such, launching, acceptance and implementation of TQM programme is nothing more than a dream for such organisations.


Comments
Post a Comment