Vapour Compression Refrigeration System
Vapour Compression Refrigeration System
Vapour-compression refrigeration or vapor-compression refrigeration system (VCRS) in which the refrigerant undergoes phase changes, is one of the many refrigeration cycles and is the most widely used method for air-conditioning of buildings and automobiles.
Vapor-compression uses a circulating liquid refrigerant as the medium which absorbs and removes heat from the space to be cooled and subsequently rejects that heat elsewhere.
History:-
1805- The American inventor Oliver Evans described a closed vapor-compression refrigeration cycle for the production of ice by ether under vacuum.
1834- American Great Britain, Jacob Perkins, built the first working vapor-compression refrigeration system in the world.
1842- American physician, John Gorrie who built a working prototype, but it was a commercial failure.
1850- American engineer Alexander Twining took out a British patent for a vapor compression system that used ether.
1851- Built a mechanical ice-making machine.
1856- The first practical vapor compression refrigeration system was built by James Harrison. who patent was for a vapor compression system using ether, alcohol or ammonia.
1859 & 1860- The first gas absorption refrigeration system using gaseous ammonia dissolved in water (referred to as "aqua ammonia") was developed by Ferdinand Carré of France in 1859 and patented in 1860.
1876- Carl von Linde, an engineering professor at the Technological University Munich in Germany, patented an improved method of liquefying gases.
1920- Ammonia, sulfur dioxide SO2, and methyl chloride (CH3Cl) use as refrigerants.
Components of Vapour Compression Refrigeration System
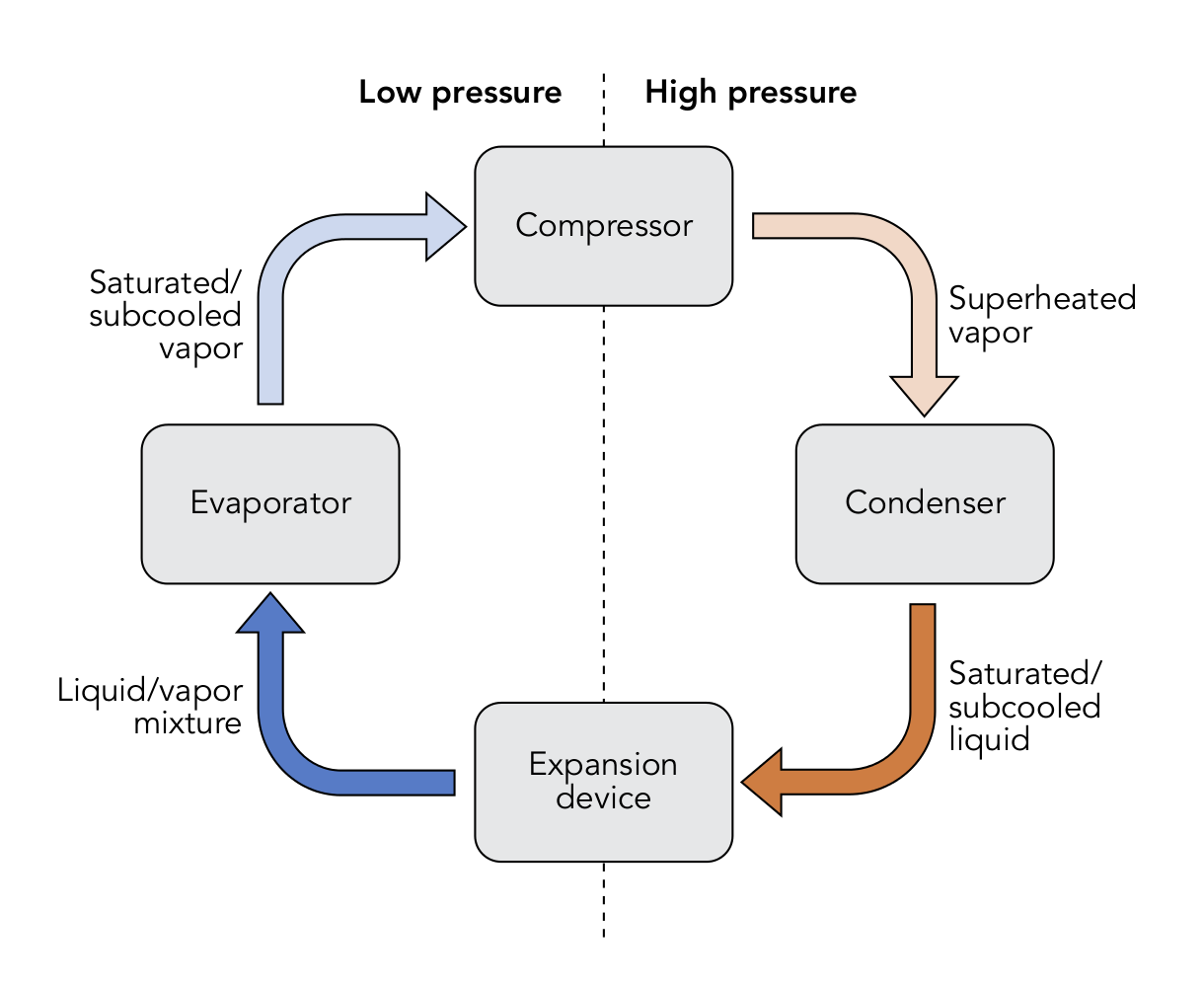
The Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle involves four components:
1. Compressor
2. Condenser
3. Expansion valve/throttle valve
4. Evaporator.
Working Process
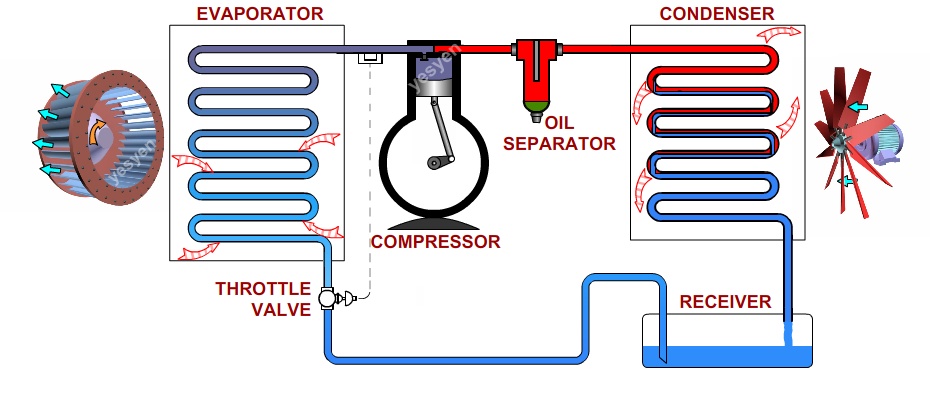
STEP 1: COMPRESSION
The refrigerant (for example R-717) enters the compressor at low temperature and low pressure. It is in a gaseous state. Here, compression takes place to raise the temperature and refrigerant pressure. The refrigerant leaves the compressor and enters to the condenser. Since this process requires work, an electric motor may be used. Compressors themselves can be scroll, screw, centrifugal or reciprocating types.
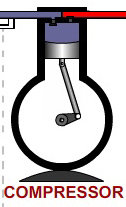
STEP 2: CONDENSATION
In the condenser the refrigerant vapor that is at higher pressure is cooled by a cooling medium available at atmospheric temperature like water or air. The condenser is the component in the refrigeration cycle where the refrigerant vapor is condensed to liquid state.
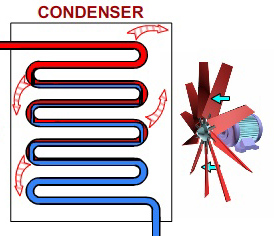
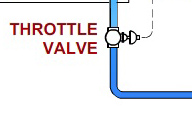
STEP 3: THROTTLING AND EXPANSION
When the refrigerant enters the throttling valve, it expands and releases pressure. Consequently, the temperature drops at this stage. Because of these changes, the refrigerant leaves the throttle valve as a liquid vapor mixture, typically in proportions of around 75 % and 25 % respectively.
Throttling valves play two crucial roles in the vapor compression cycle. First, they maintain a pressure differential between low- and high-pressure sides. Second, they control the amount of liquid refrigerant entering the evaporator.
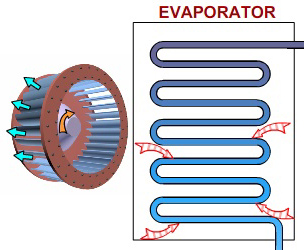
STEP 4: EVAPORATION
At this stage of the Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle, the refrigerant is at a lower temperature than its surroundings. Therefore, it evaporates and absorbs latent heat of vaporization. Heat extraction from the refrigerant happens at low pressure and temperature. Compressor suction effect helps maintain the low pressure.There are different evaporator versions in the market, but the major classifications are liquid cooling and air cooling, depending whether they cool liquid or air respectively.

- At point 1 in the diagram, the circulating refrigerant enters the compressor as a saturated vapor.
- From point 1 to point 2, the vapor is isentropically compressed (i.e., compressed at constant entropy) and exits the compressor as a superheated vapor.
- From point 2 to point 3, the superheated vapor travels through part of the condenser which removes the superheat by cooling the vapor.
- Between point 3 and point 4, the vapor travels through the remainder of the condenser and is condensed into a saturated liquid.
- Between points 4 and 5, the saturated liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve and undergoes an abrupt decrease of pressure. That process results in the adiabatic flash evaporation and auto-refrigeration of a portion of the liquid (typically, less than half of the liquid flashes). The adiabatic flash evaporation process is isenthalpic (i.e., occurs at constant enthalpy).
- Between points 5 and 1, the cold and partially vaporized refrigerant travels through the coil or tubes in the evaporator where it is totally vaporized by the warm air (from the space being refrigerated) that a fan circulates across the coil or tubes in the evaporator. The evaporator is where heat is absorbed from the space being cooled by transfer from the warm air in the space.
- The evaporator operates at essentially constant pressure. The resulting saturated refrigerant vapor returns to the compressor inlet at point 1 to complete the thermodynamic cycle.
Refrigeration application
|
Short descriptions
|
Typical refrigerants used
|
|---|---|---|
Domestic refrigeration
|
Appliances used for keeping food in dwelling units
| |
Commercial refrigeration
|
Holding and displaying frozen and fresh food in retail outlets
| |
Food processing and cold storage
|
Equipment to preserve, process and store food from its source to the wholesale distribution point
| |
Transport refrigeration
|
Equipment to preserve and store goods, primarily foodstuffs, during transport by road, rail, air and sea
| |
Electronic cooling
|
Low-temperature cooling of CMOS circuitry and other components in large computers and servers
|
Problem in Vapour Compression Refrigeration system
1. Compressor Leakage/Failure
The Compressor failure due to lubrication problems, overheating, slugging, flood back and contamination.
The Compressor failure due to lubrication problems, overheating, slugging, flood back and contamination.
2. Fouling- Evaporator & Condenser
Fouling is any insulator hinders transfer between the water and the refrigerant.It could result from algae growth, sedimentation, scale formation or slime. As this problem increases head pressure, it can lead to increased energy use by the compressor.
Fouling is any insulator hinders transfer between the water and the refrigerant.It could result from algae growth, sedimentation, scale formation or slime. As this problem increases head pressure, it can lead to increased energy use by the compressor.
3. Motor Cooling
The motor is easily the highest energy consumer in the vapor compression cycle. Most times when efficiency drops in this device, it is because of a cooling problem. Many issues could lead to this- blocked air filters, dirty air passages etc.
4. Liquid Line Restriction
The liquid line restricted due to encounter low evaporator pressure.
The motor is easily the highest energy consumer in the vapor compression cycle. Most times when efficiency drops in this device, it is because of a cooling problem. Many issues could lead to this- blocked air filters, dirty air passages etc.
4. Liquid Line Restriction
The liquid line restricted due to encounter low evaporator pressure.
Advantages of Vapour Compression Refrigeration System
1. COP of the system is quite high.
2. For same refrigeration effect the evaporator size is small in compare to Air Compression Cycle.
3. Volume of refrigerant calculated is low. Hence running cost is low.
4. The operating temperature range is huge.
5.The temperature of the evaporator easily controlled by regulating controlled valve.
2. For same refrigeration effect the evaporator size is small in compare to Air Compression Cycle.
3. Volume of refrigerant calculated is low. Hence running cost is low.
4. The operating temperature range is huge.
5.The temperature of the evaporator easily controlled by regulating controlled valve.
Disadvantages of Vapour Compression Refrigeration System
1. Initial cost is high.
2. Inflammability, leakage & toxicity.
2. Inflammability, leakage & toxicity.



This information has many things to read and I am glad to read more impressive information about it. Thank you so much for the share..You can visit this site
ReplyDeleteSupermarket Refrigeration Systems
I am glad from your comment. Your valuable suggestions are also always welcome.😊
DeleteMajanos heating contractor has been providing affordable and reliablerefrigeration repair services in your Los Angeles.
ReplyDeleteThank you for shearing such a helpful blog. I also want to suggest you something The Hubs provides widest range of commercial refrigerator for supermarket which can be used for food storage purposes, cooling large amount of eatables etc. If anyone looking for a commercial refrigerator for supermarket in Singapore then visit the hubs.
ReplyDelete