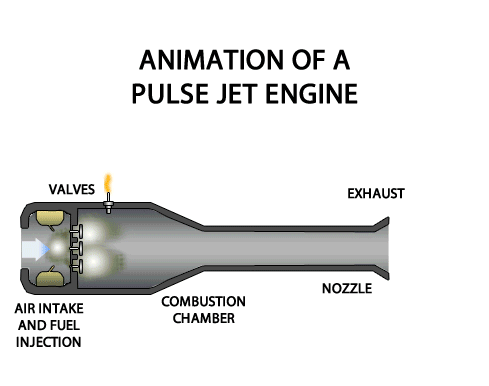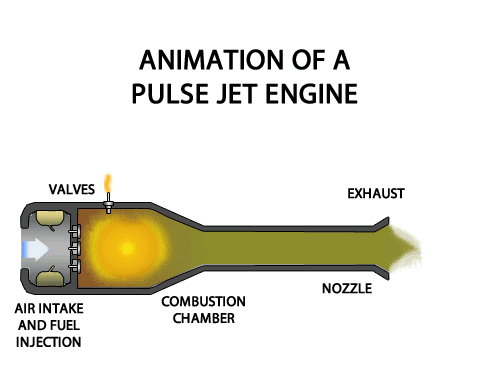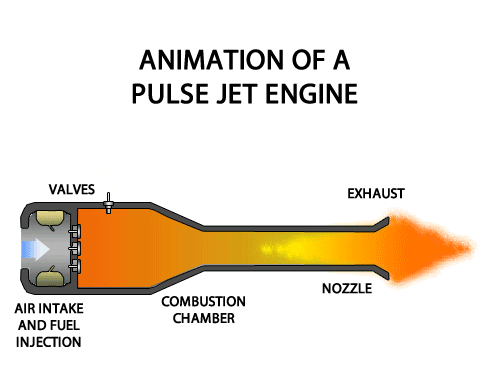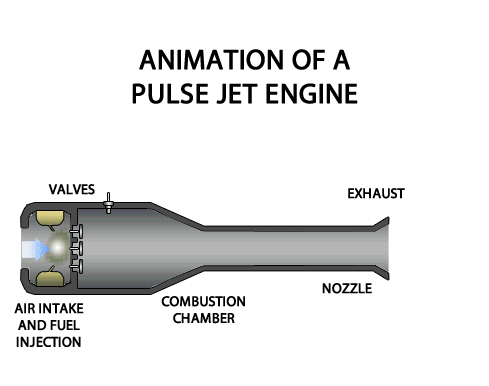
TURBOFAN ENGINE

TURBOFAN ENGINE The turbofan engine is a combination of the turbo prop and the turbojet engines combining the advantages of both. The turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a portmanteau of "turbine" and "fan": the turbo portion refers to a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical energy from combustion, and the fan, a ducted fan that uses the mechanical energy from the gas turbine to accelerate air rearwards. Thus, whereas all the air taken in by a turbojet passes through the combustion chamber and turbines, in a turbofan some of that air bypasses these components. In the 1950s, Rolls-Royce introduced the first turbofan in the world, namely, RB.80 Conway. Classification 1. According to Fan Location (a) Forward Fan Turbofan Engine (b) AFT Fan Turbofan Engine 2. According to Spools (a) Single Spool Turbofan Engine (b) Double Spool Turbofan Engine (c) Triple Spool Turb...